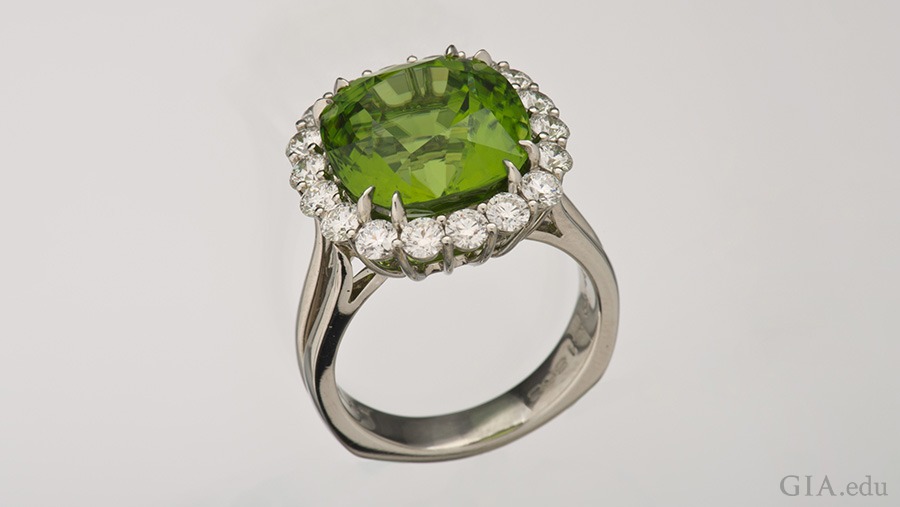
The yellow-green peridot, found in lava, meteorites and deep in the Earth’s mantle, is an extreme gem
The ancient Egyptians called Peridot a “gem of the sun” and believed it had fallen from heaven. The truth is that olivine is a common component of meteorites.
Peridot is the name for the gemstone variety of olivine. It is a common mineral in basalts, but also in kimberlites, which “bring” diamonds to the Earth’s surface. The most valuable feature of peridot in transparent crystals is its unique color, which changes from light yellow to olive green.
The most beautiful peridotes are located in Egypt on its islands in the Red Sea. In Europe, the period in the Kozákov locality in northern Bohemia had an exceptional position in the Middle Ages. The Egyptians already made and wore peridotite beads 3,500 years ago. The most beautiful collection was collected during the Ottoman Empire by Turkish sultans. Today, these peridotites are on display at the Topkapi Museum in Istanbul. From the middle of the 19th century. appears in jewelry and reached its peak of popularity during the Victorian era during the reign of Edward VII. England, who called it his favorite gem.
The largest ground peridot, 311.78 ct (62.35 g), was found on the island of Zagbargad in Egypt and is now located in the Smithsonian Museums in the United States. A relatively large 192.75 ct called peridot is in the Diamond Fund in Moscow.